Medial Bicipital Groove Borders

The medial bicipital groove is seen on the surface anatomy of the upper arm it is formed by the longitudinal hollow between the biceps and triceps muscles.
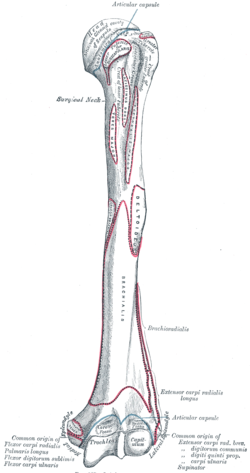
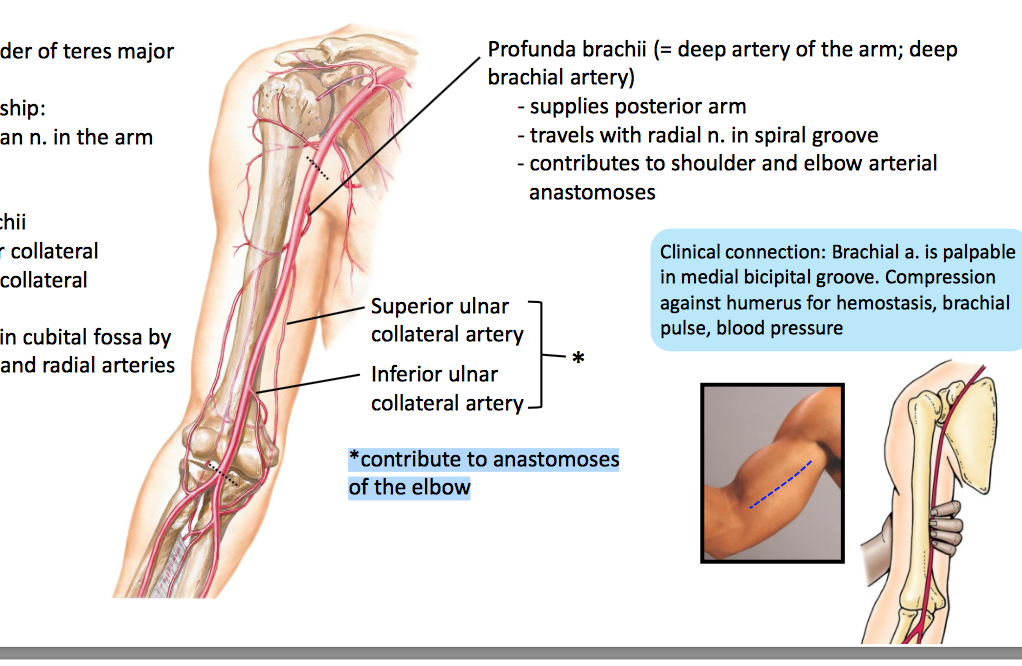
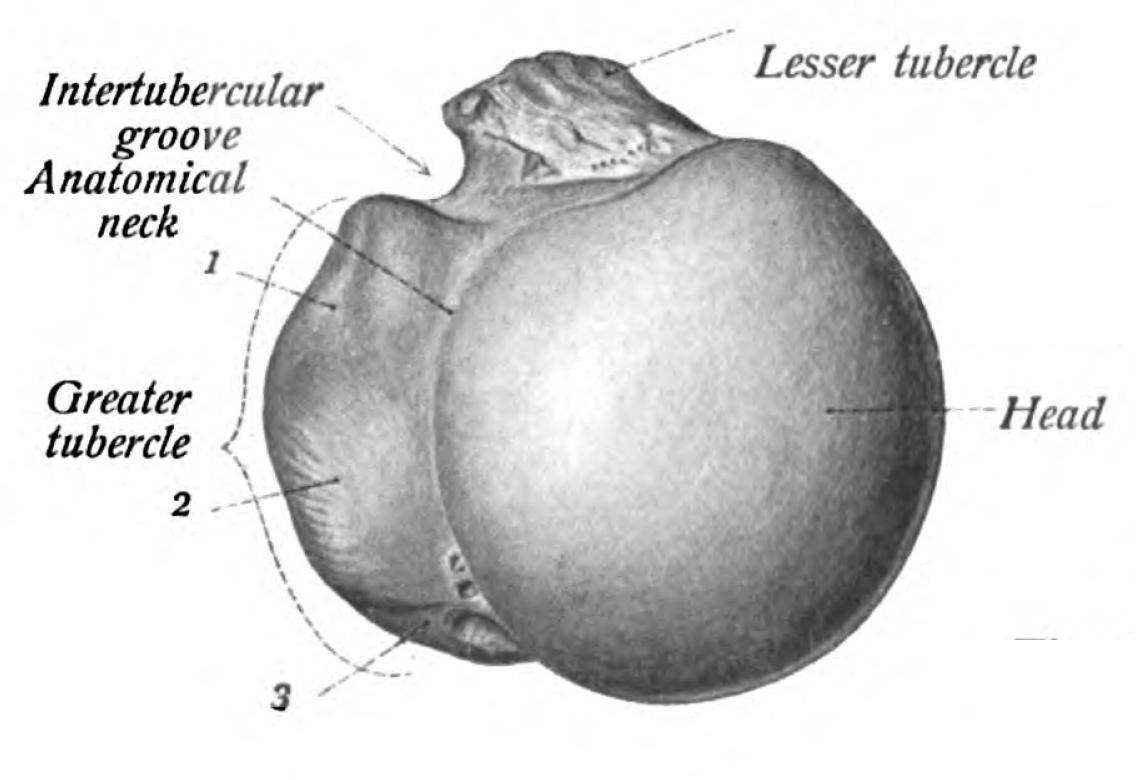
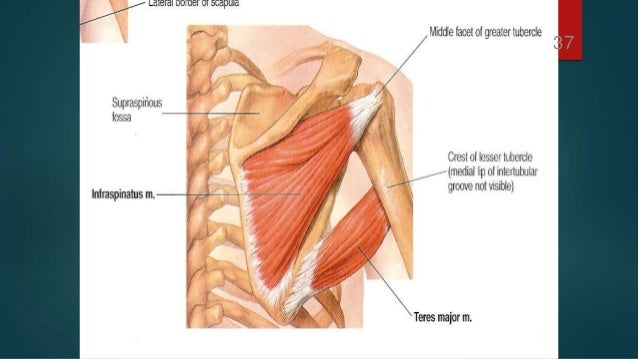
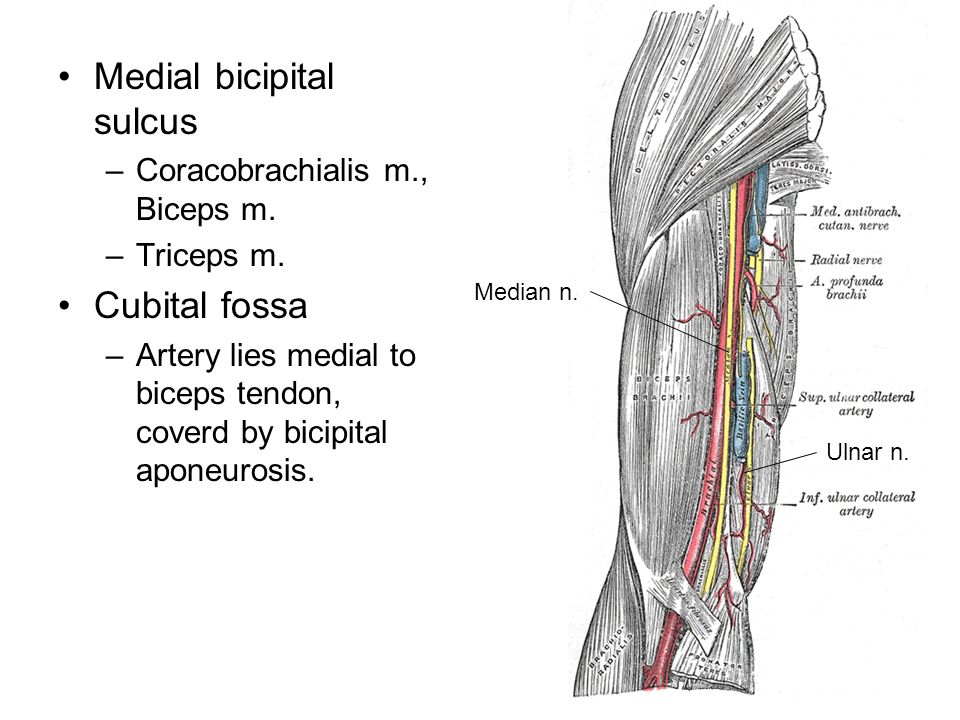
Medial bicipital groove borders. Inferolateral cutaneous nerve of arm posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm lateral hhead of triceps medial head of triceps anconeus. The intertubercular groove or also known as the bicipital sulcus is a deep groove that begins between the two tubercles and extends longitudinally down the proximal shaft of the humerus. Goes through triangular interval with profunda brachii a and wraps around humerus shaft in the spiral groove from medial to lateral deep to triceps in the groove it gives off 3 branches. D groeve a groove between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus for passage of the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle.
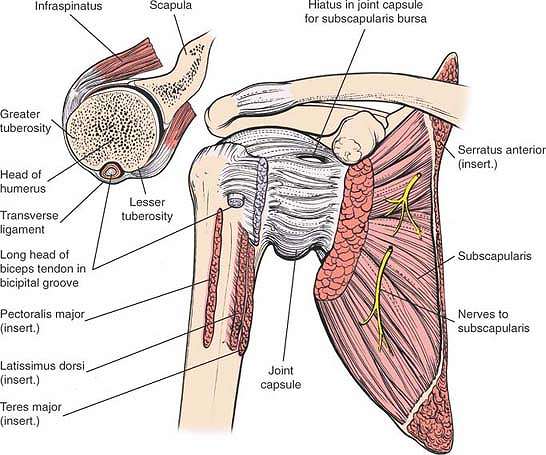
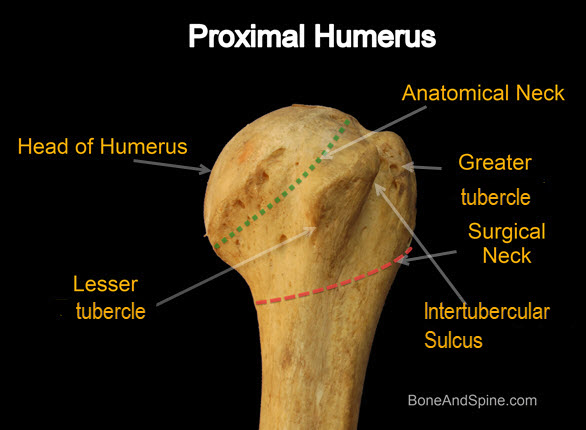
It should be distinguished from the bicipital groove or intertubercular sulcus which is not a surface anatomy structure. This is the area between the medial border of the humerus to the line drawn as a continuation of the crest of the greater tubercle. Sectioning exposed the infraclavicular neurovascular structures including the transition between the subclavian and axillary vessels and the brachial plexus fascicles as well as the distribution of its terminal branches in the axillary fossa and medial bicipital groove of the arm fig. Illustrated anatomical parts with images from e anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures.
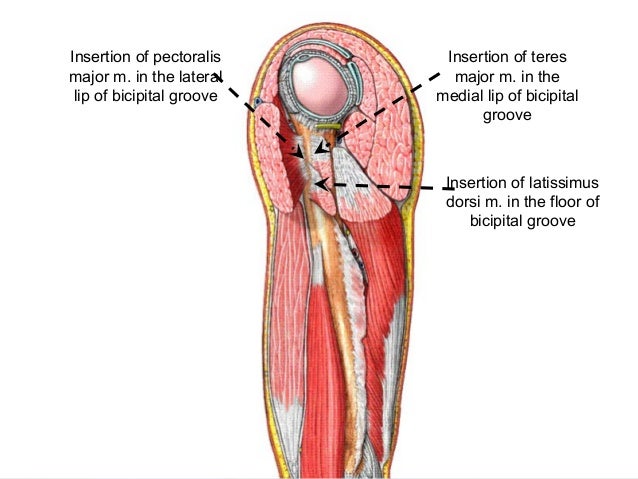
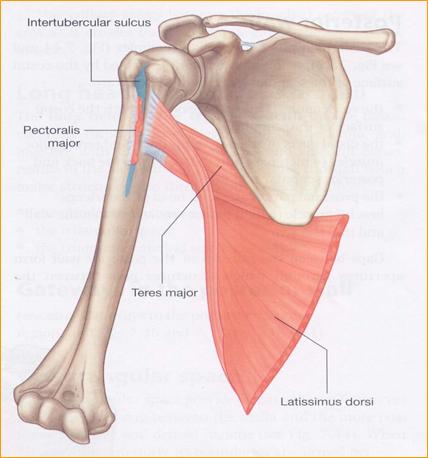
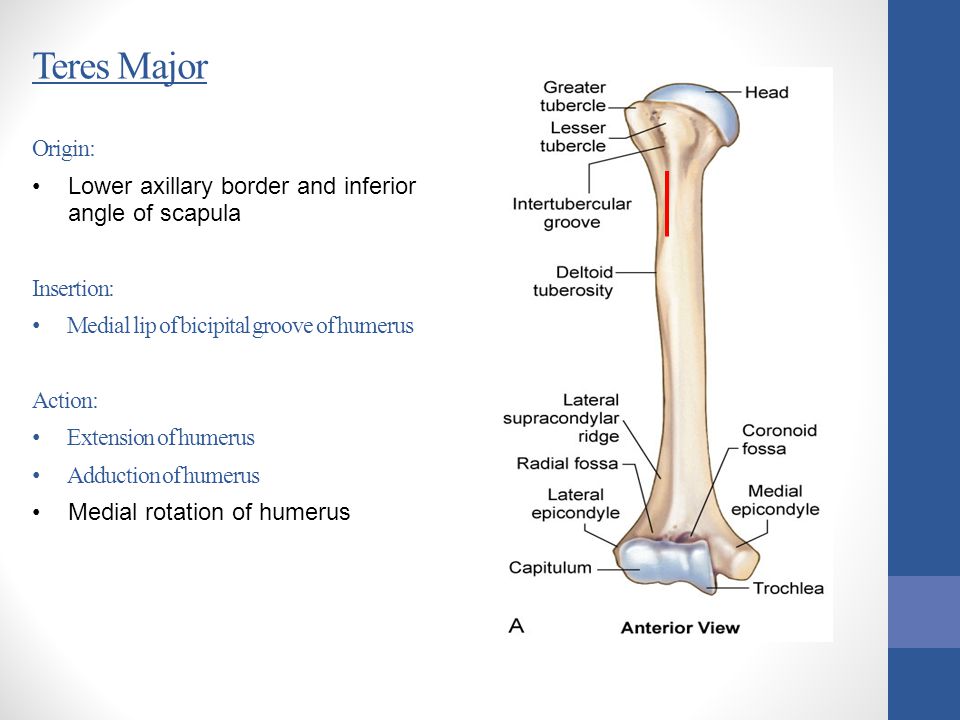
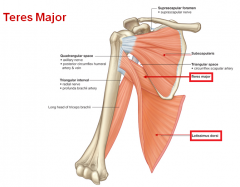
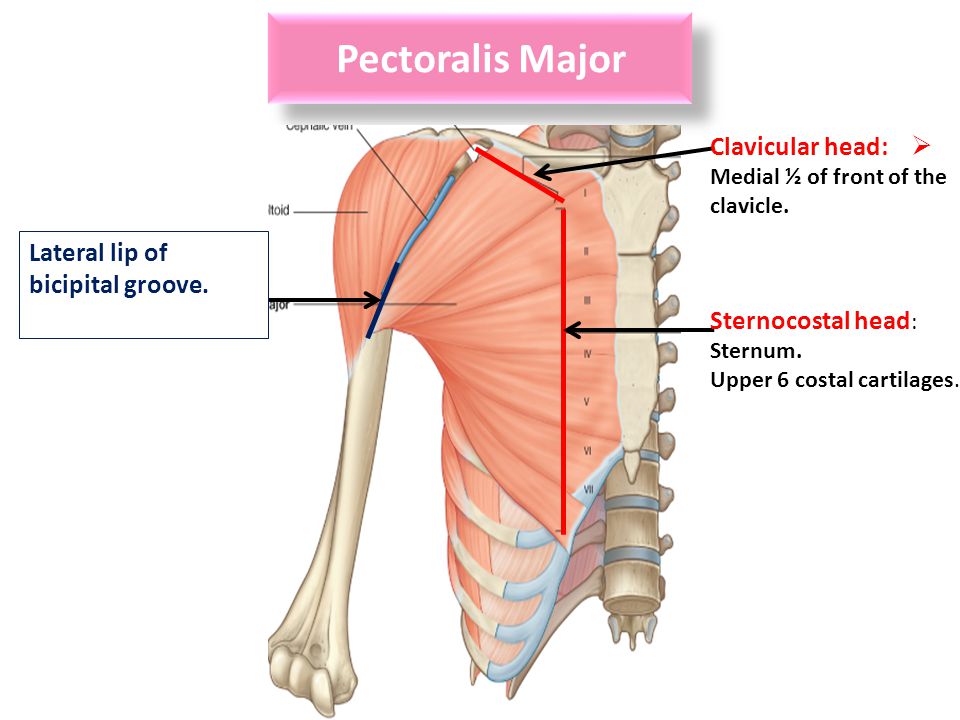
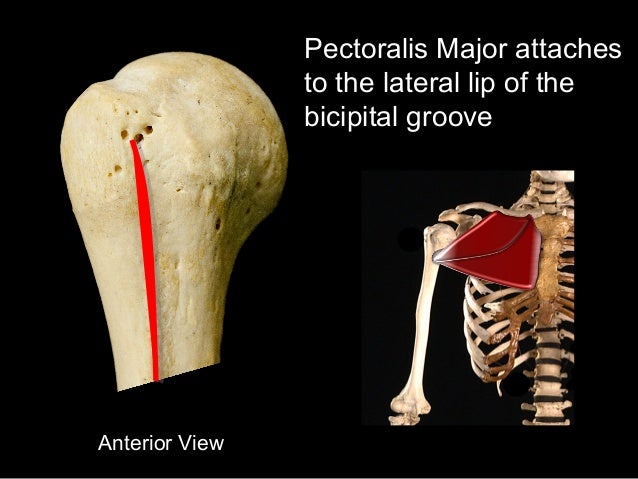
Medial border and inferior angle of scapula. Medial bicipital groove sulcus bicipitalis medialis. Insertion of pectoralis major. L bis twice caput head.
The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip. The anteromedial surface is the area between the medial border of the humerus to the line drawn as a continuation of the crest of the greater tubercle. The pulse of the brachial artery can be felt in the medial bicipital groove. Medial and lateral pectoral nerve of brachial plexus nerve supply of pectoralis major.
Sulcus bicipitalis ulnaris anatomical parts. The intertubercular groove or also known as the bicipital sulcus is a deep groove that begins between the two tubercles and extends longitudinally down the proximal shaft of the humerus. Insertion of serratus anterior. Coracoid process of scapula.