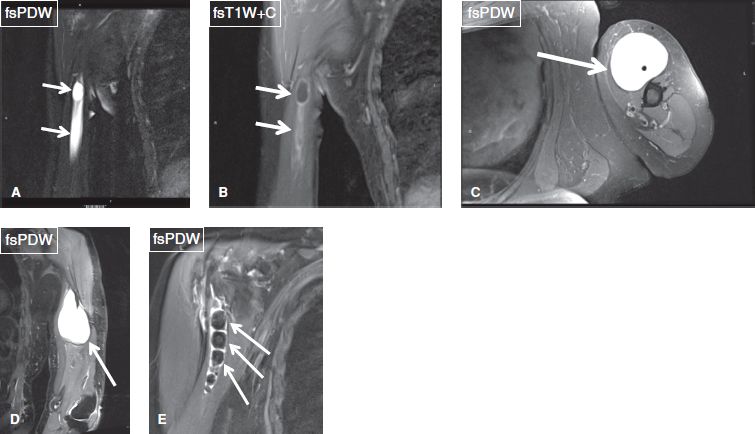
Bicipital Groove Cyst
Non specific as it communicates with the glenohumeral joint.
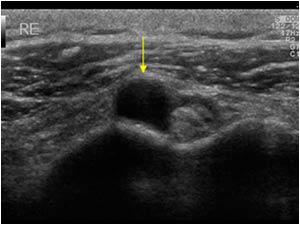
Bicipital groove cyst. Thickening or thinning of the tendon. A positive test consists of pain elicited in the bicipital groove when the patient attempts to forward elevate the shoulder against examiner resistance. Longitudinal image of the biceps tendon. The mass was more palpable after the arthrogram.
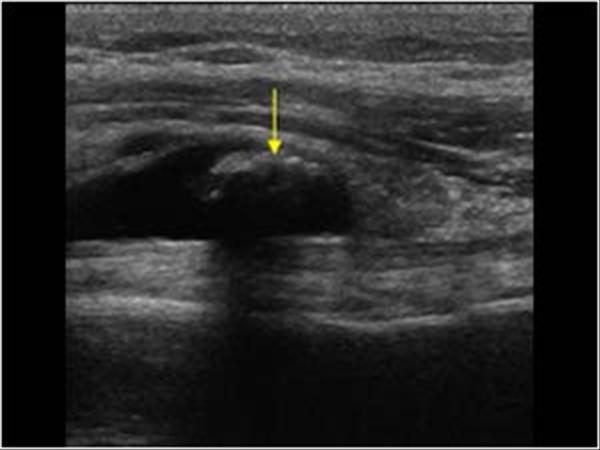
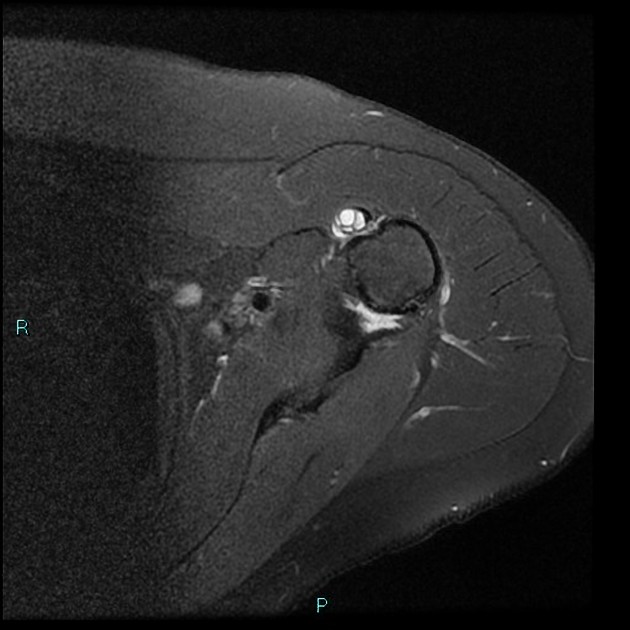
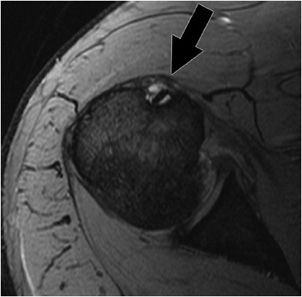
Radiographic assessment of the humerus revealed the presence of an osseous cyst like lesion ocll in the lateral intertubercular groove within the proximal humerus figs 1 2 and 3. Intra articular ganglion cyst originating from the intertubercular groove. 1 axial t1 weighted mr image shows shallow bicipital groove in presence of congenital absence of biceps tendon arrow. Another longitudinal image of the biceps tendon with the cystic looking mass anterior.
Duplication of the lhbt is a diagnostic dilemma in mri of patients with shoulder pain. We concluded that the mass was a synovial cyst due to chronic synovitis. Another transverse image of the bicipital groove. Figure 1 2 and 3 demonstrating the osseous cyst like lesion in the lateral intertubercular groove of the humerus blue arrow.
We report a very rare case of intra articular ganglion cyst of the long head of the biceps tendon that originated from the bicipital groove as a rare cause of shoulder pain. Is the mass anterior of the biceps tendon a cyst or something else. Irregularity of the tendon. Although it may look like a cyst it is a calcification in its resorbing phase.
Direct palpation over the patient s bicipital groove elicits a painful response in the setting of pathology. The elbow is slightly flexed and the. Ganglion cysts commonly occur around the shoulder mostly in the spinoglenoid and suprascapular notches. An arthrogram of the left shoulder joint demonstrated extension of dye down the bicipital groove and into the mass in the upper arm.