Bicipital Medial Groove
Medical definition of bicipital groove.
Bicipital medial groove. The depth width and medial wall angle have been studied in relation to overall bicipital groove stability with significant variability recognized in. Of or relating to a biceps. The subscapularis sparing approach in humeral head replacement. Having two heads or points of origin as a muscle.
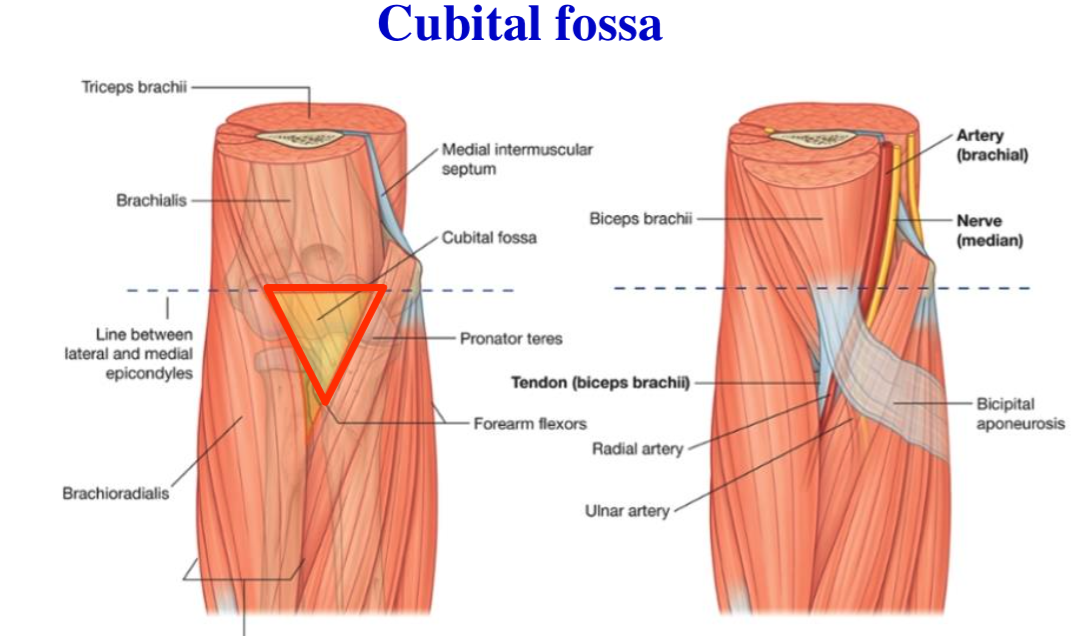
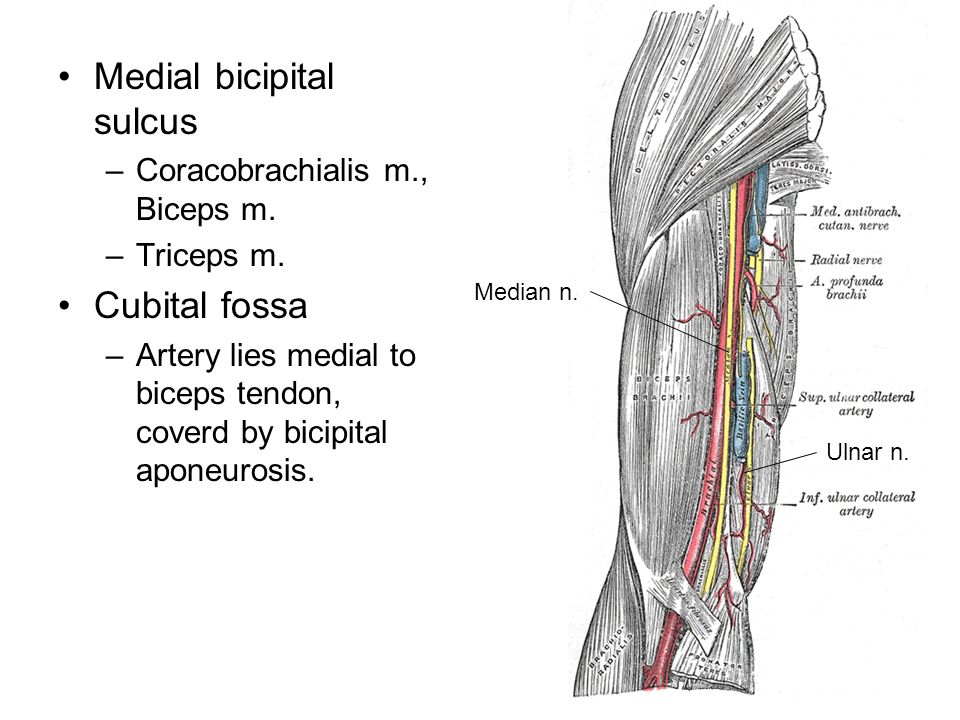
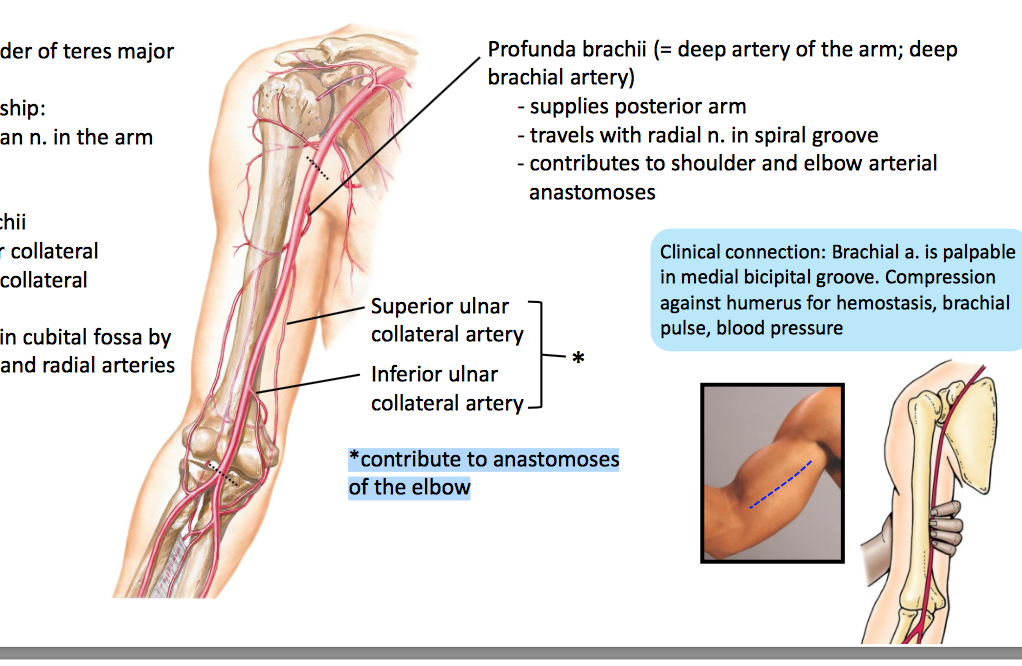
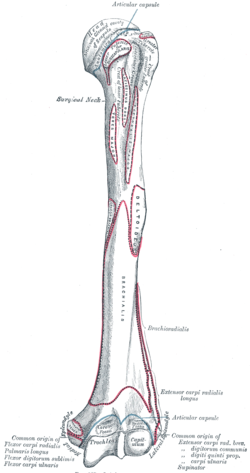
It contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle which is ensheathed in a synovial reflection of the. Caput head bicipital bī sĭp ĭ tl adj. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral. The pulse of the brachial artery can be felt in the medial bicipital groove.
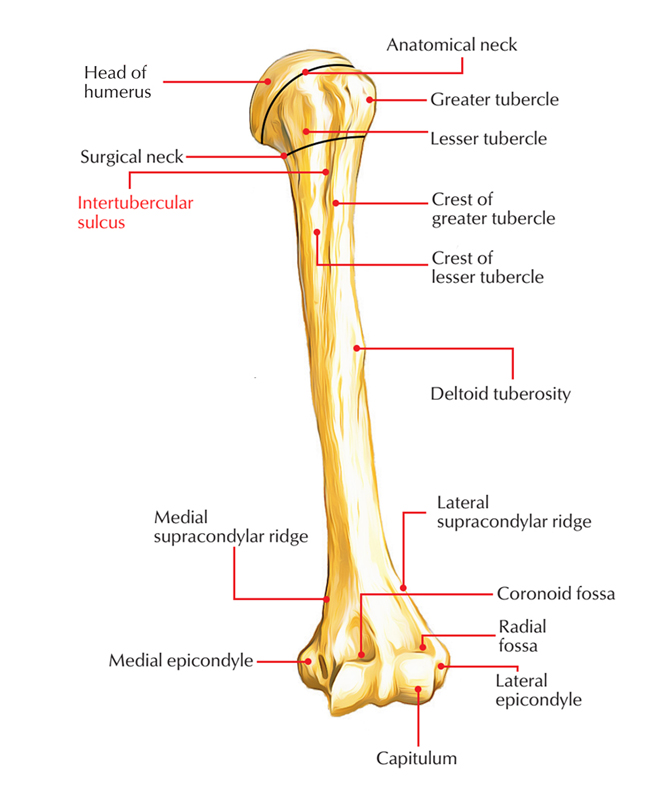
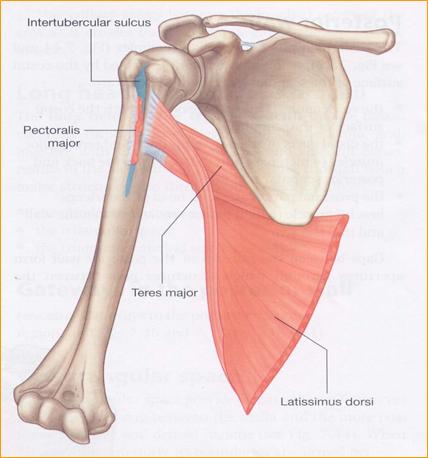
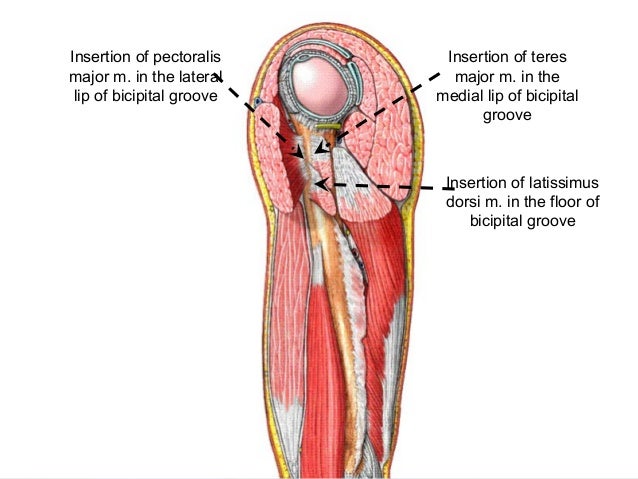
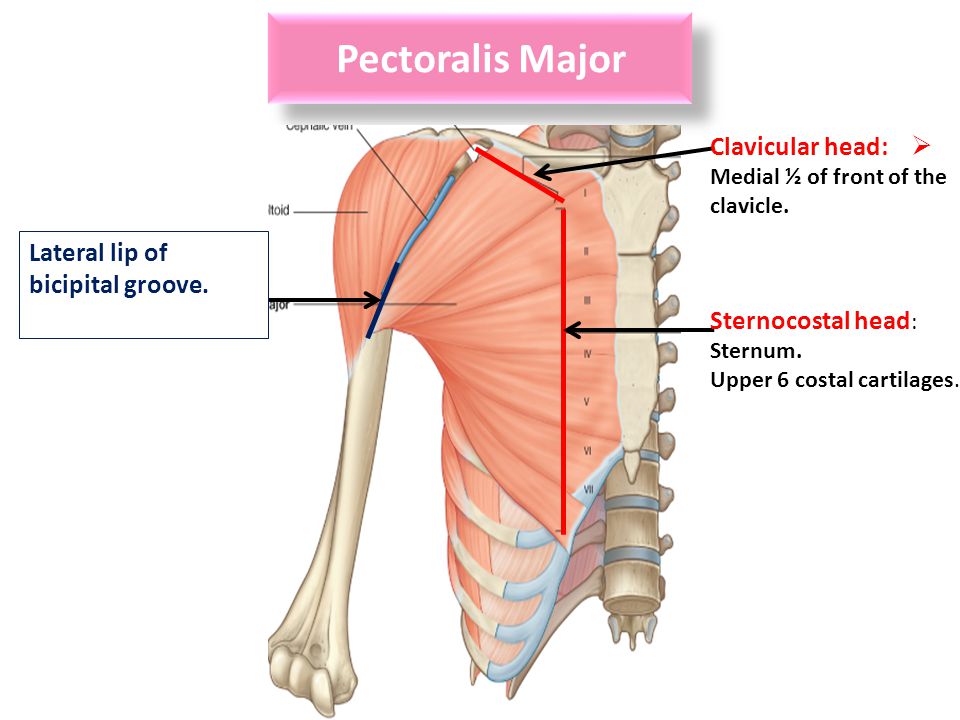
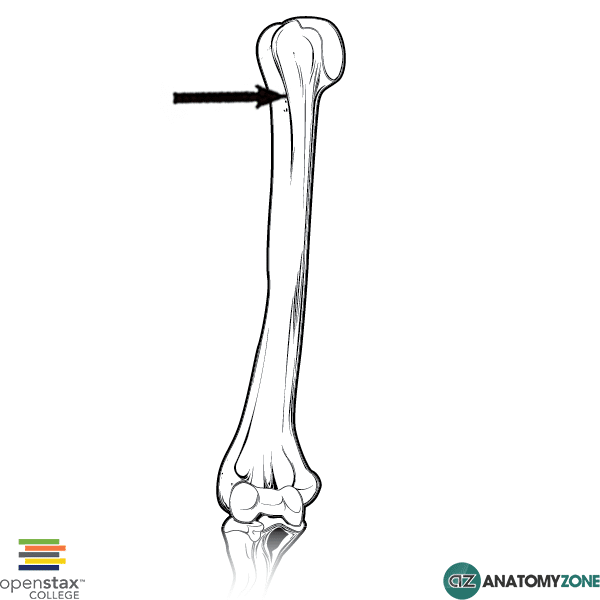
Pectoralis major to lateral lip of groove. The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1. L bis twice caput head. D groeve a groove between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus for passage of the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle.
It should be distinguished from the bicipital groove or intertubercular sulcus which is not a surface anatomy structure. The initiating point for the inferior takedown is along the medial ridge of the bicipital groove. Bicipital bi sip ĭ t l having two heads. Submitted by nishanth koda on sat 23 08 2008 19 27.
Mobilisation of adhesions at posterior shoulder and lh of biceps in the bicipital groove should be included in the rehabilitation process. Bicipital adjective referring to 2 heads or origins of a. Relating to a biceps muscle. Teres major attaches to medial lip of groove.
The medial bicipital groove is seen on the surface anatomy of the upper arm it is formed by the longitudinal hollow between the biceps and triceps muscles. A furrow on the upper part of the humerus occupied by the long head of the biceps called also intertubercular groove. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral. The bicipital groove is an anatomic landmark that sits between the greater and lesser tuberosities and its osseous and soft tissue components contribute to the inherent stability of the lhbt.
Pertaining to a biceps muscle. The bicipital groove also known as the intertubercular sulcus or sulcus intertubercularis is the indentation between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus that lodges the biceps tendon. The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip.