Bicipital Groove Edema Mri

Mri allows for visualization of the long head of the biceps tendon.
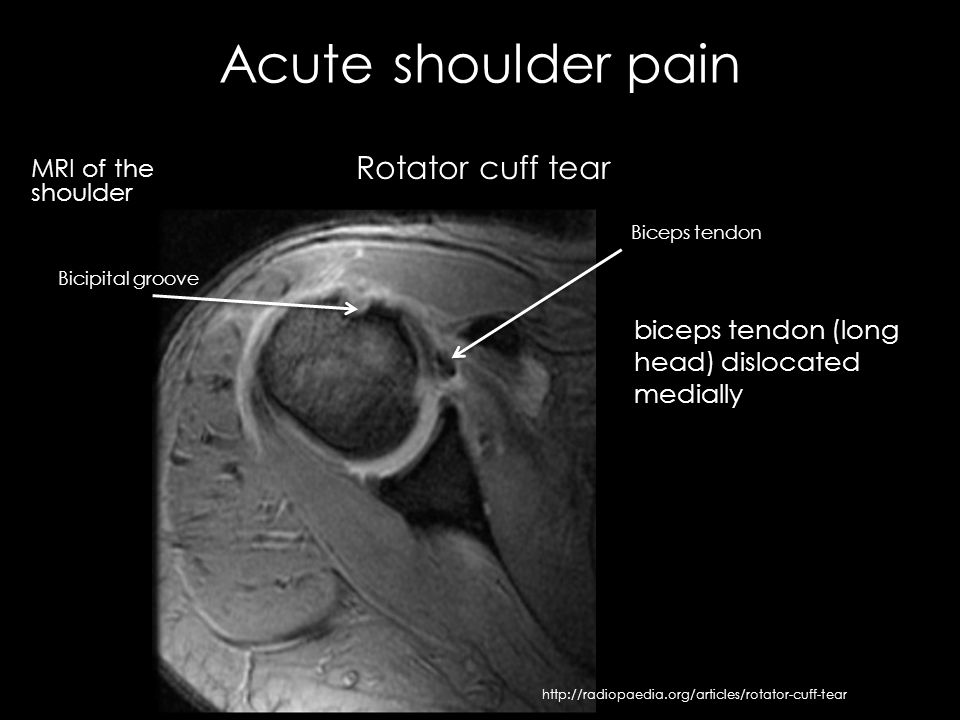
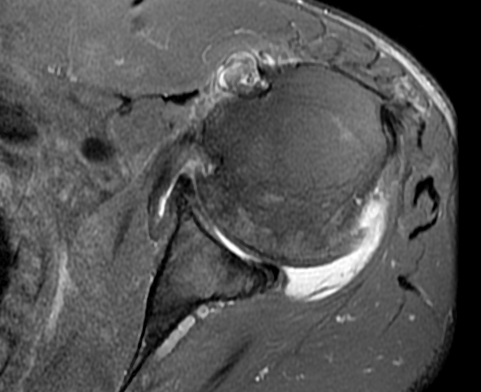
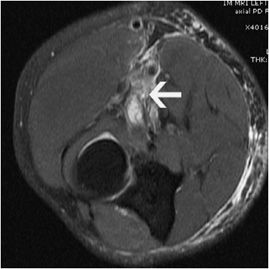
Bicipital groove edema mri. Thickened with intermediate high t2 signal intensity noted at the supraspinatus tendon suggestive of tendinosis. Mri is most beneficial in delineating other associated shoulder pathologies. Magnetic resonance imaging mri is useful in evaluating the lhb tendon bicipital groove and any fluid or edema that may be indicative of pathology. The translucent screw can be seen at mri.
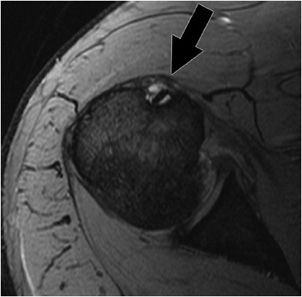
The bicipital groove is an osseous groove formed in the humeral head by the medial and lateral tuberosities. This should not be mistaken for a cyst or tumor. In this project we investigate the relationship between the 3d shape of the bicipital groove and the incidence of pathology of the long biceps tendon. It serves to retain the long head of the biceps brachii.
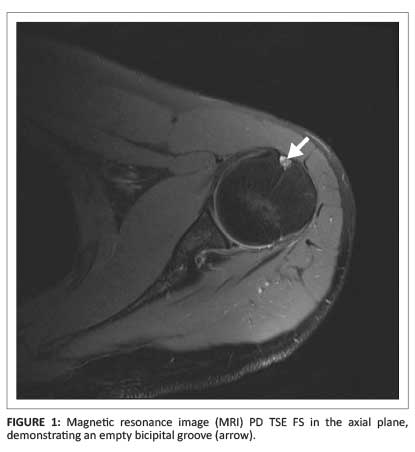
However there is poor concordance with mri suspected pathology intra operative findings and or histologic grades of. High t2 signal intensity noted at the of this humeral head at the biceps groove. Abnormalities seen may include degenerative changes and splits within the tendon and in the case of subluxation displacement from its normal position within the bicipital groove. Magnetic resonance imaging mri is useful in evaluating the lhbt bicipital groove and any fluid or edema that may be indicative of pathology.
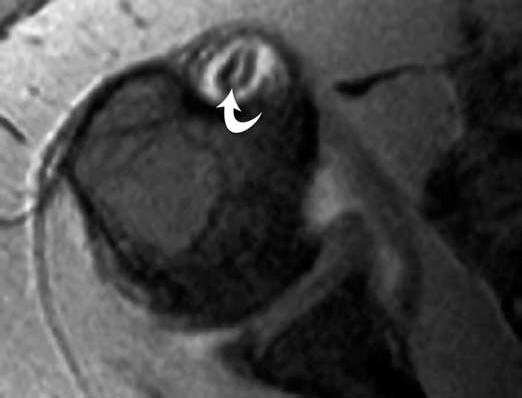
The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1. At mri the biceps tendon is seen to be attached to the humeral shaft. High t2 fluid signal intensity is noted around the thickened biceps tendon which is seen within its groove suggestive of tenosynovitis. It contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle which is ensheathed in a synovial reflection of the.
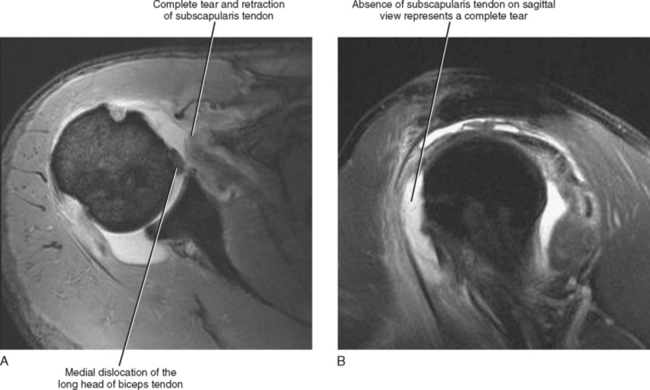
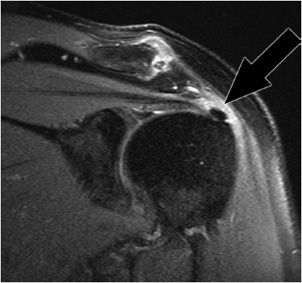
Biceps tendinitis is a disorder of the tendon around the long head of the biceps muscle. It is often not possible to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 lesions at mri and in both cases the biceps tendon is often perched on the lesser tuberosity. When only the medial sheath is torn type 2 the biceps tendon is also allowed to sublux medially within the bicipital groove. Inflammation of the biceps tendon within the intertubercular bicipital groove is called primary biceps.
Glenohumeral capsular edema is noted. The bicipital groove also known as the intertubercular sulcus or sulcus intertubercularis is the indentation between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus that lodges the biceps tendon. Mri helps define other associated shoulder pathologies and in the setting of lhbt instability particular attention should be given to evaluating for concomitant subscapularis injury.