Bicipital Groove Injection Ultrasound

The ultrasound guided shoulder injection trainer allows trainees to acquire the key skills in locating injecting and aspirating the 4 most commonly treated shoulder sites.
Bicipital groove injection ultrasound. Safety considerations will also be highlighted including the use of doppler imaging to avoid anterior circumflex artery injection. A subacromial injection is preferred in this population because it avoids direct needle penetration of the tendon. Biceps bicipital tendonitis is an inflammation of the long head of the biceps tendon as it passes through the bicipital groove of the anterior humerus see image below. 8 on clinical examination provocative tests such as the speed and yergason tests are used to elicit bicipital groove pain suggestive of lbht origin 9 stone and adler biceps peritendinous injections by a rotator interval approach 2290 j ultrasound med 2015.
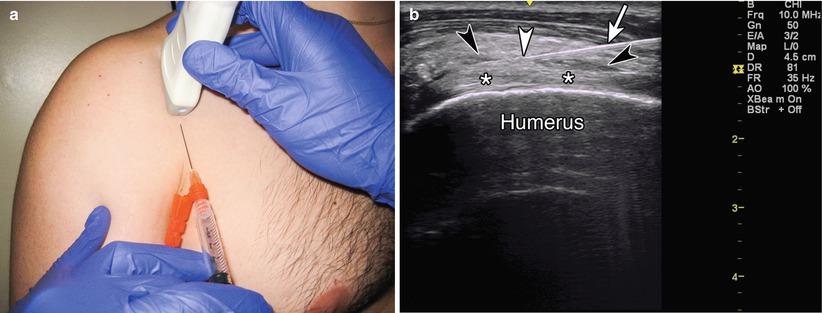
The needle should enter the skin at 30 and be directed parallel to the groove. Once you locate the appropriate injection site mark the injection site. Scan the area at the point of maximum tenderness to find the appropriate injection site. Glenohumeral joint subacromial space acromiaclavicular joint bicipital groove.
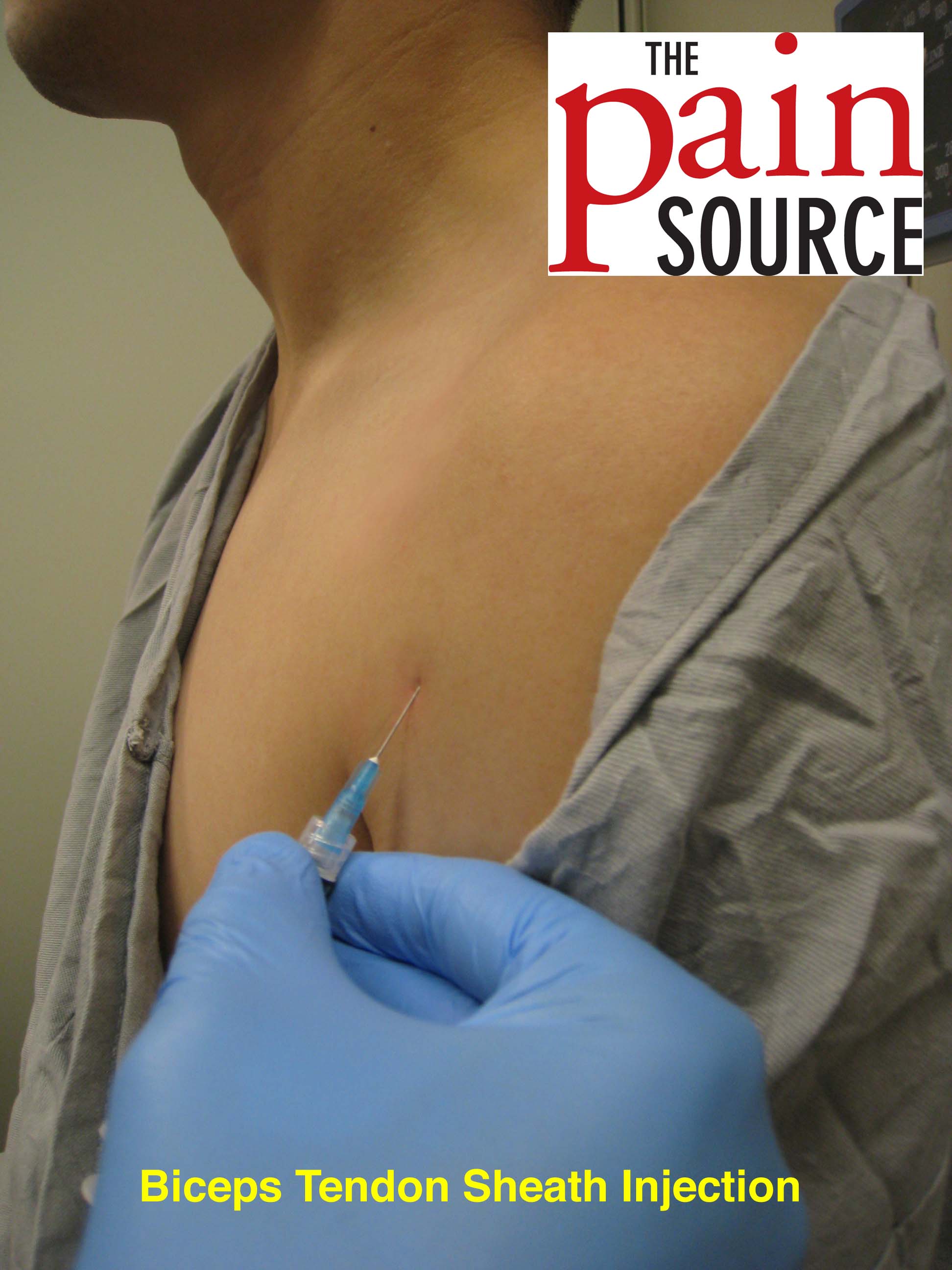
If there is fluid in the biceps tendon sheath when extra articular you can inject at that site. Ultrasound guided injection technique for bicipital tendonitis clinical perspectives the musculotendinous units of the shoulder are subjected to an amazing variation of stresses as they perform their function of allowing a full range of motion of the shoulder while at the same time providing shoulder stability. The model uses ultrasound material that contains properties similar to human tissue. File5966 repetitive lifting and to a lesser extent overhead reaching lead to inflammation microtearing and if untreated degenerative change.
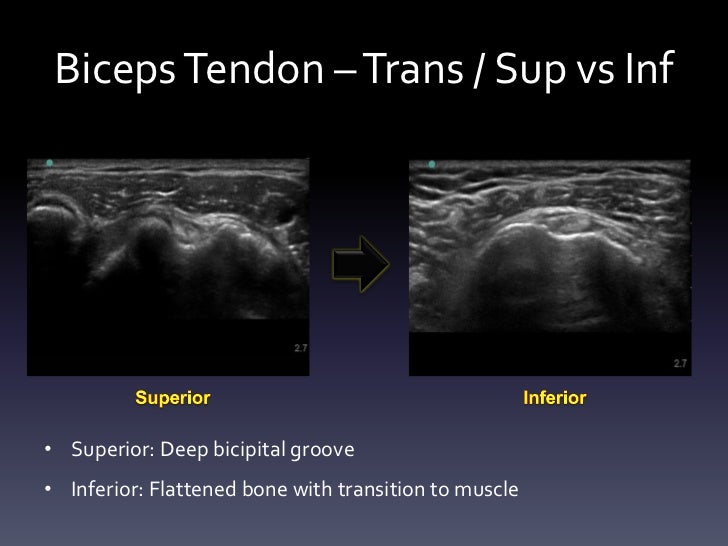
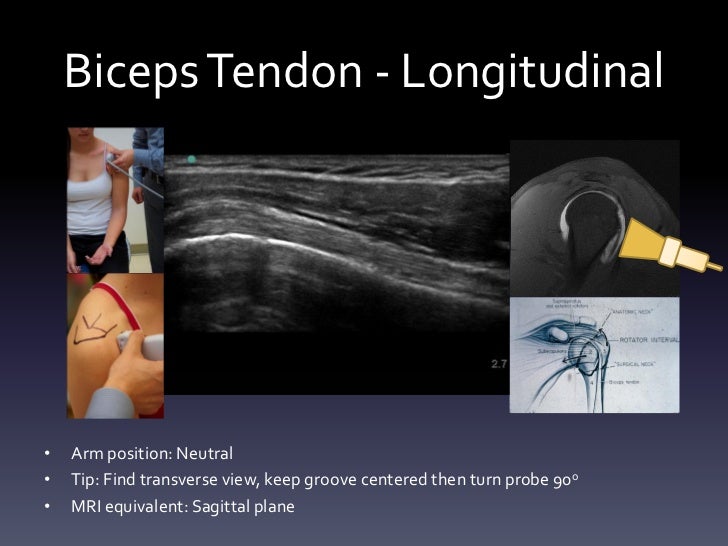
The relatively poor blood supply limits the ability of these. Scan patient looking at the biceps tendon short axis transverse extra articular and at the rotator interval. Ultrasound guided injection at the rotator. With the patient sitting or lying the biceps tendon is identified in the groove and the point of insertion noted.
To inject into the area of the long head of the biceps tendon the needle is inserted directly into the most tender area over the bicipital groove. The risk of tendon rupture is greater in patients aged 50 years and older. Place the high frequency linear us probe at the bicipital groove with the probe marker pointing to patient s right side.