Bicipital Groove Function
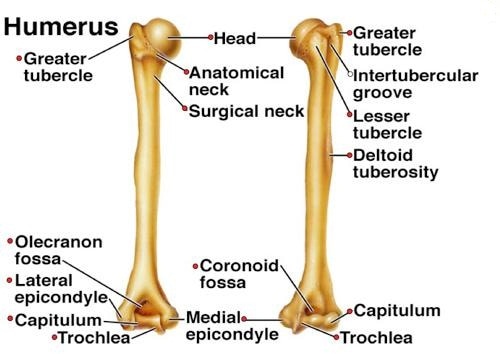
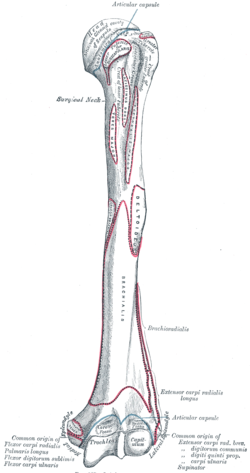
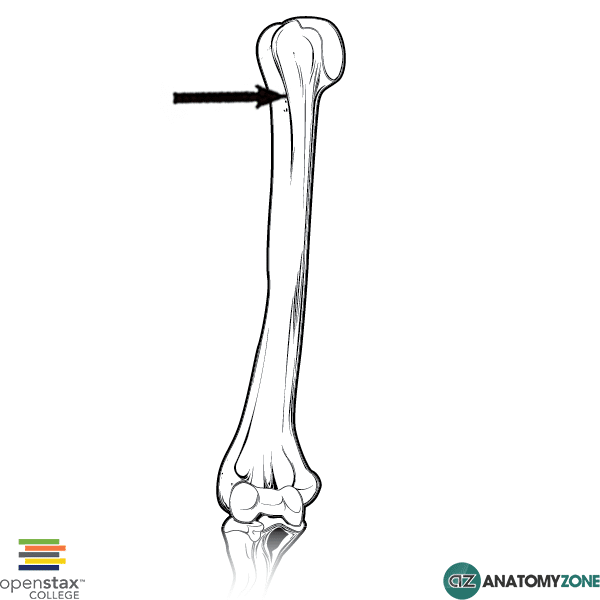
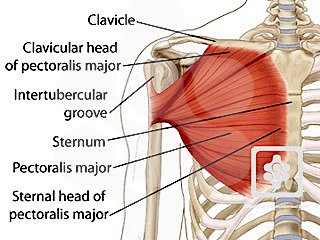
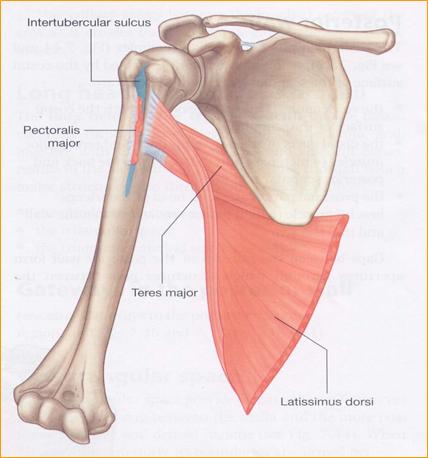
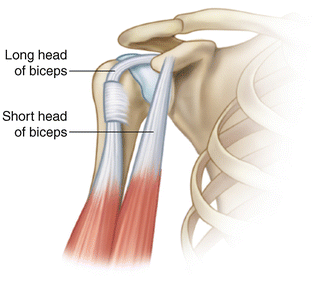
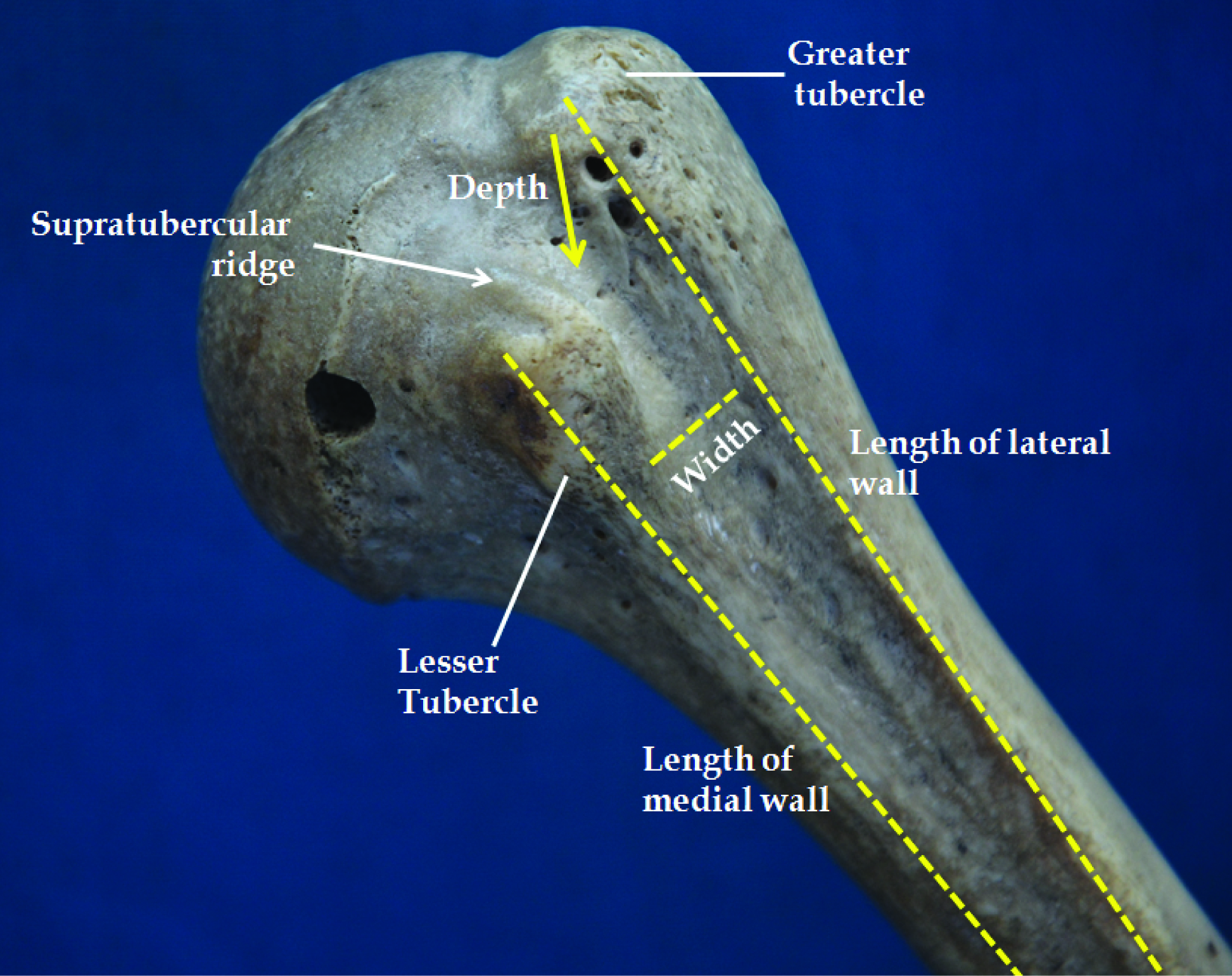
The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip.
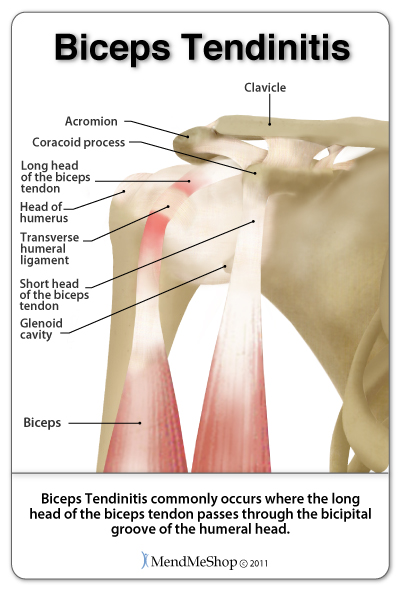
Bicipital groove function. The biceps is a large muscle situated on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. The tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle runs in this groove and attaches on the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. Bicipital tendinitis or biceps tendinitis is an inflammatory process of the long head of the biceps tendon and is a common cause of shoulder pain due to its position and function. The intertubercular sulcus also known as the intertubercular groove or bicipital groove is a groove separating the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus.
The structure indicated is the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral. The biceps brachii muscle biceps is a large thick muscle of the arm consisting of two heads. Also known by the latin name biceps brachii meaning two headed muscle of the arm the muscle s primary function is to flex the elbow and rotate the forearm the heads of the muscle arise from the scapula shoulder blade and combine in the middle arm to form a muscle mass.
Other functions unclear hypotheses include. Humeral head depressor during abduction. The greater and lesser tubercles of humerus are separated from each other by a deep groove the intertubercular groove bicipital groove which lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii and transmits a branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery to the shoulder joint it runs obliquely downward and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone. Originates at the supraglenoid tubercle above the glenoid cavity of the scapula it lies within the intracapsular space but it still remains extrasynovial.
Exits shoulder joint within bicipital groove under transverse humeral ligament. Primary function is to stabilize humeral head in glenoid during elbow flexion and forearm supination. The long biceps tendon makes a sharp turn at the humeral head and continues its course in the bicipital groove intertubercular sulcus. The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip.
While the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints. Bicipital aponeurosis a radiating triangular band of fibrotendinous tissue that obliquely traverses the ulnar hollow of the elbow and merges with the forearm s deep fascia. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral. The bicipital aponeurosis provides a tissue plane that protects the brachial artery and median nerve in phlebotomy of local veins.
Flexor and abductor of shoulder.