Medial Bicipital Groove Boundaries

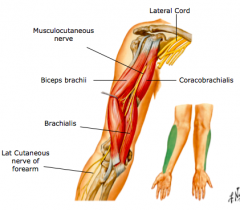
The long head of biceps brachii muscle runs along this groove.
Medial bicipital groove boundaries. In this article we shall look at the borders and contents of the cubital fossa including any clinical relevance. The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. Hence the bicipital groove faces ventrally and the bicipital tendon even in the normal position is pressed against the medial wall of the intertubercular sulcus. The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1.
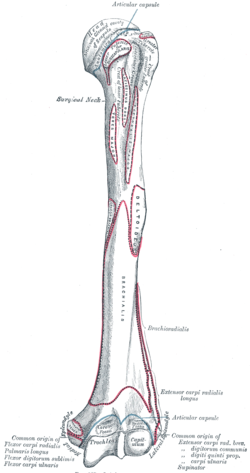
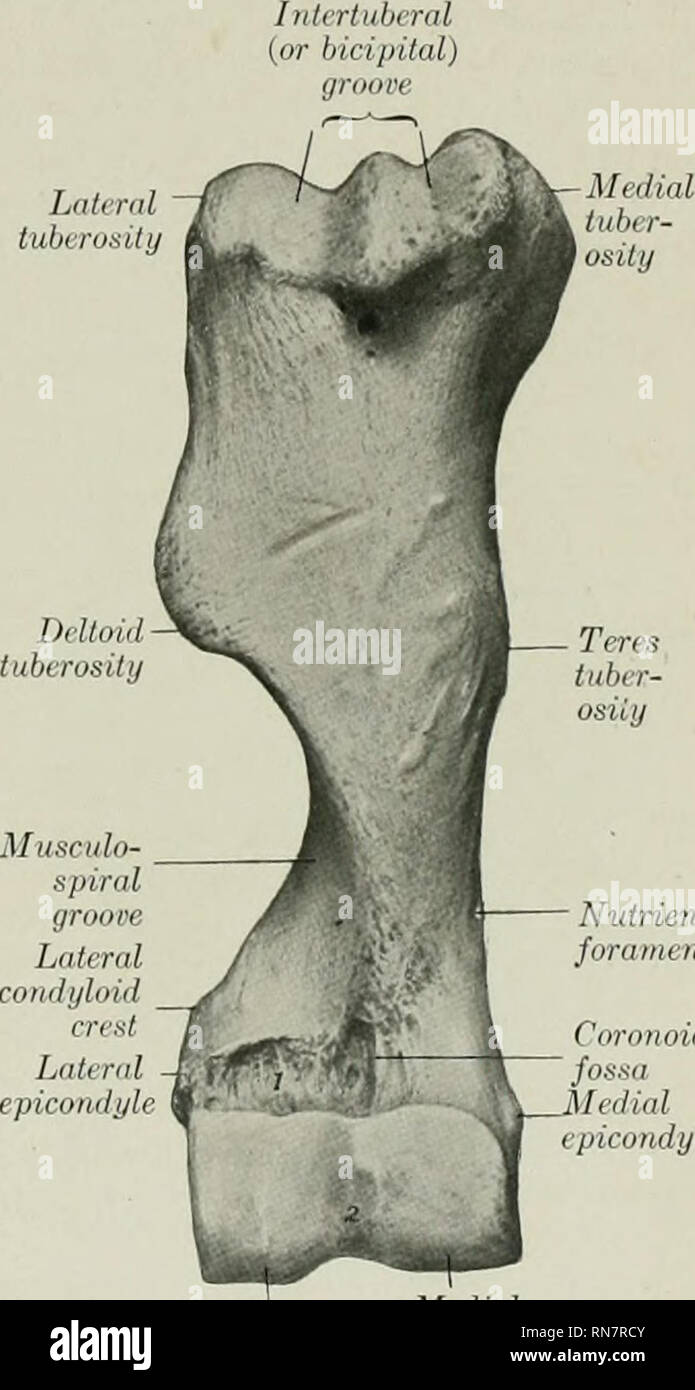
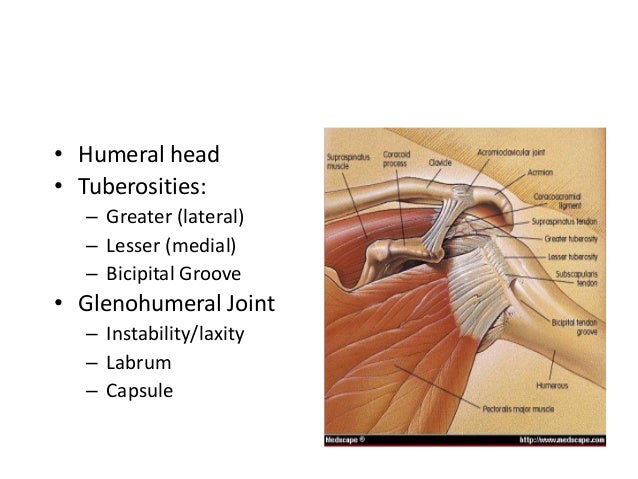
The intertubercular groove or also known as the bicipital sulcus is a deep groove that begins between the two tubercles and extends longitudinally down the proximal shaft of the humerus. The medial bicipital groove is seen on the surface anatomy of the upper arm it is formed by the longitudinal hollow between the biceps and triceps muscles. The transverse humeral ligament connects the lesser and greater tubercles. The depth width and medial wall angle have been studied in relation to overall bicipital groove stability with significant variability recognized in.
The long biceps tendon lbt sits within the bg. Goes through triangular interval with profunda brachii a and wraps around humerus shaft in the spiral groove from medial to lateral deep to triceps in the groove it gives off 3 branches. Dislocation of the long head of biceps tendon is one of the complications of shoulder injury. The bicipital groove also known as the intertubercular sulcus or sulcus intertubercularis is the indentation between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus that lodges the biceps tendon.
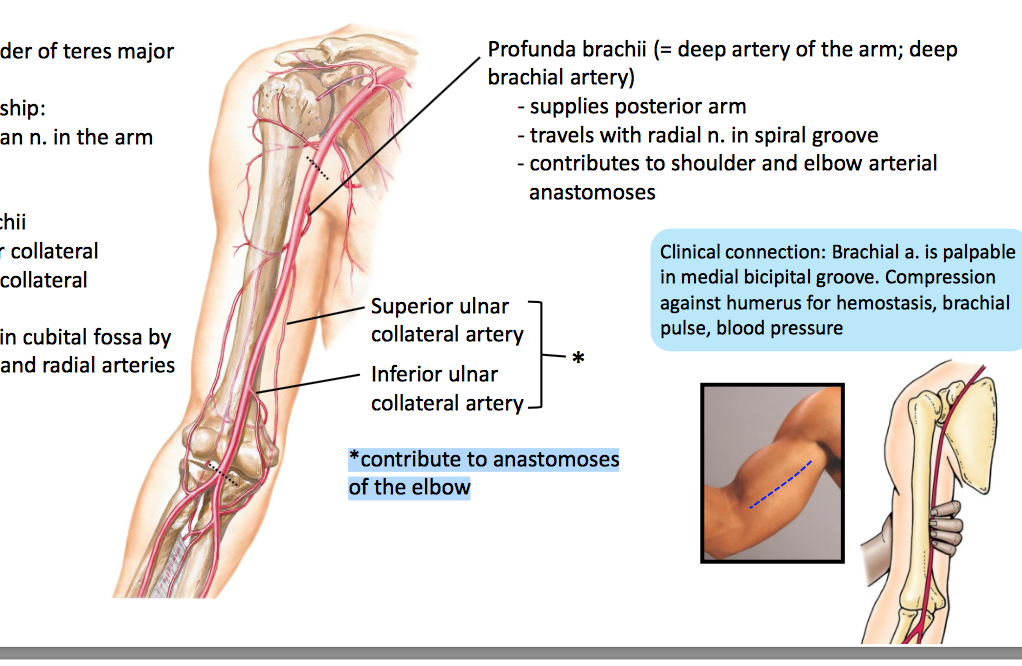
It contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle which is ensheathed in a synovial reflection of the. The pulse of the brachial artery can be felt in the medial bicipital groove. Secondly the medial wall of the bicipital groove is often inadequately developed with a slanting wall that offers only a tiny fulcrum for the tendon. The long head of biceps lhb tendon is usually located inferiorly in the bicipital groove held there by the biceps pulley the stabilization role of the transverse humeral ligament is controversial 3 as it moves superiorly it arches through the rotator cuff interval where it is held by a sling.
The bg prevents the lbt from dislocating during movement of the arm. It should be distinguished from the bicipital groove or intertubercular sulcus which is not a surface anatomy structure. Inferolateral cutaneous nerve of arm posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm lateral hhead of triceps medial head of triceps anconeus. It is located as a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint.
The bicipital groove bg of the proximal humerus is a groove in the humeral head formed by the medial and lateral tuberosities fig.