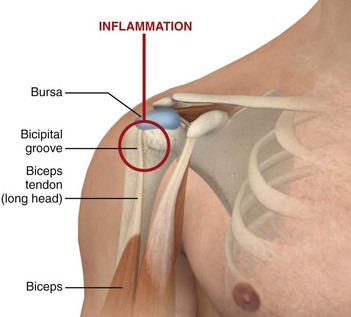
Bicipital Groove Point Tenderness
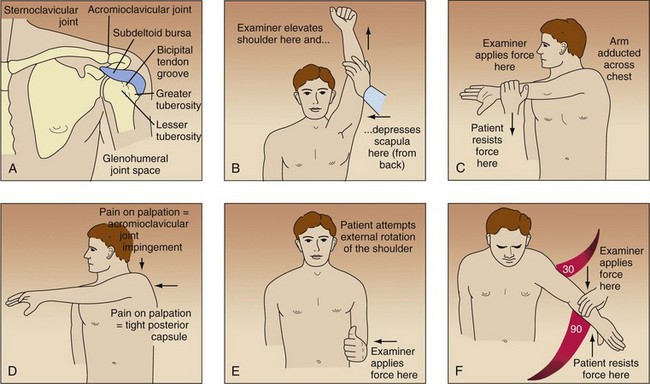
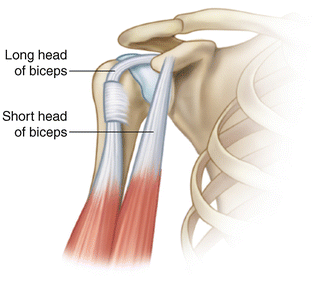
The tendon is palpated in the bicipital groove of the humerus.
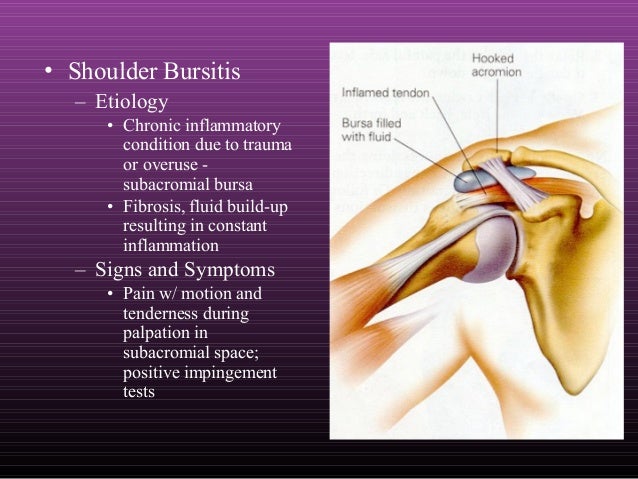
Bicipital groove point tenderness. Comparing the contralateral shoulder is helpful. Biciptal tendinitis is a typical overuse sports injury and is common amongst athletes who perform an action that places strain on the shoulder. The needle should enter the skin at 30 and be directed parallel to the groove. Without this finding it is extremely unlikely the lhb is involved in the patient s symptoms.
After a sterile prep and subcutaneous local anesthetic infiltration a 25 gauge 1 5 or 2 in needle is inserted into the skin over the area of maximum tenderness and directed into the groove at an angle near parallel to the groove itself. Local anesthetic injections into the biceps tendon sheath may be therapeutic and diagnostic. Point tenderness should move in conjunction with the bicipital groove as the examiner rotates the affected arm. To inject into the area of the long head of the biceps tendon the needle is inserted directly into the most tender area over the bicipital groove.
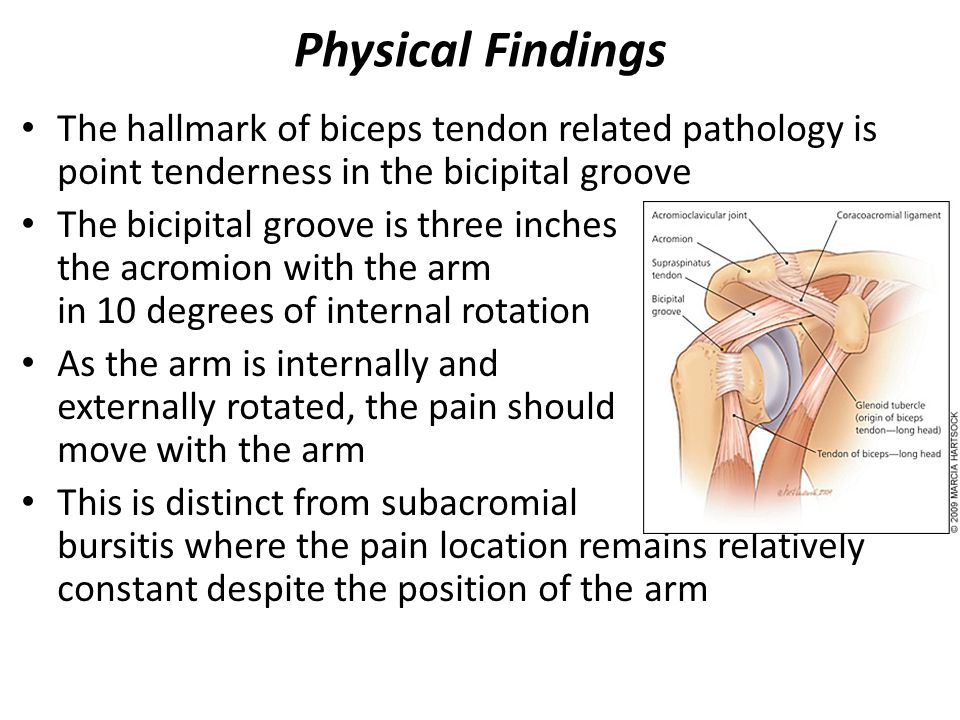
The most common isolated clinical finding in biceps tendinitis is bicipital groove point tenderness with the arm in 10 degrees of internal rotation. With the patient sitting or lying the biceps tendon is identified in the groove and the point of insertion noted. With bicipital tendinitis point tenderness with palpation of long head tendon at the bicipital groove is common. Repetitive overhead motion of the arm initiates or exacerbates the symptoms.
The hallmark of biceps tendon related pathology is point tenderness in the bicipital groove. The tendon is exposed on the anterior shoulder as it passes through the humeral bicipital groove and inserts onto the superior aspect of the labrum of the glenohu. The most common isolated clinical finding in biceps tendinitis is bicipital groove point tenderness with the arm in 10 degrees of internal rotation. Repetitive overhead motion of the arm initiates or exacerbates the symptoms.
Local anesthetic injections into the biceps tendon sheath may be therapeutic and diagnostic. The most common finding of biceps tendon injury is bicipital groove point tenderness 1 during physical examination the patient stands or sits with the arm at his or her side in 10 degrees of. Bicipital groove point tenderness is the most common isolated finding during physical examination of patients with biceps tendinitis.