Bicipital Groove Nerve

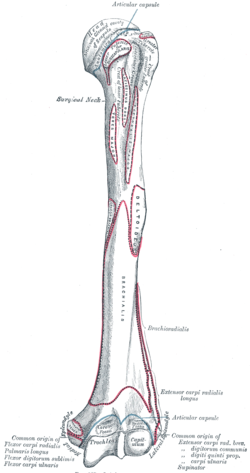
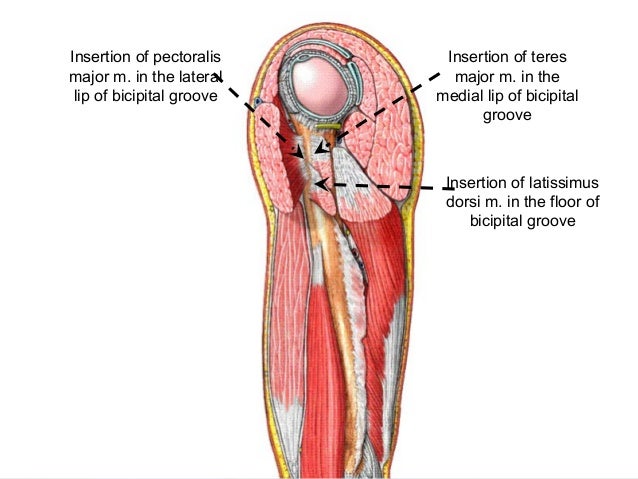
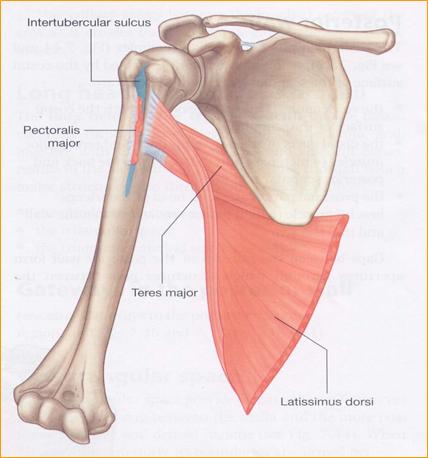
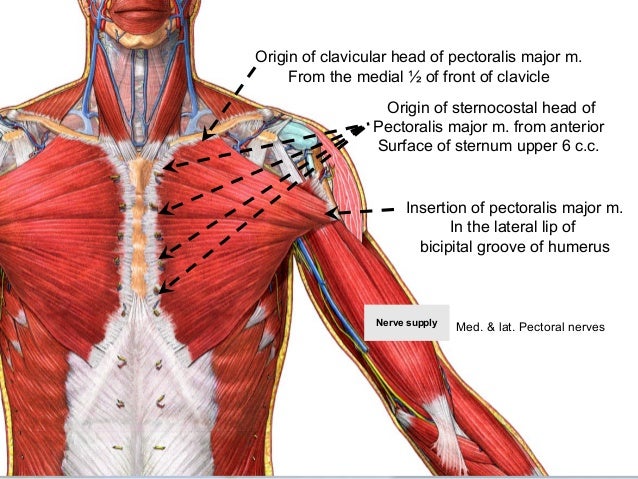
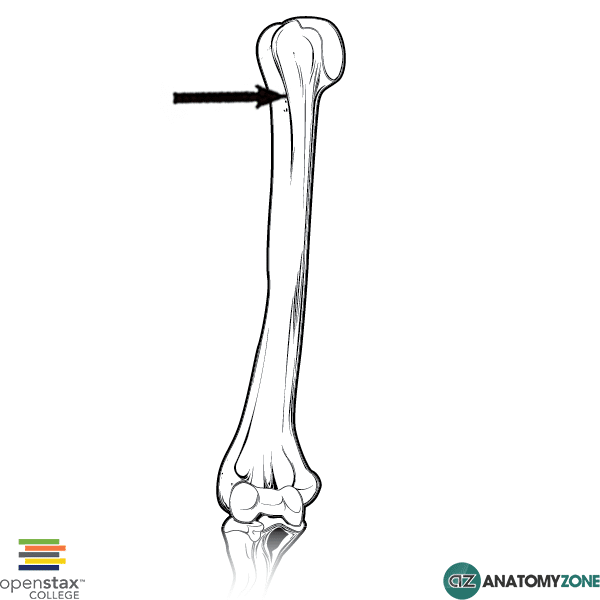
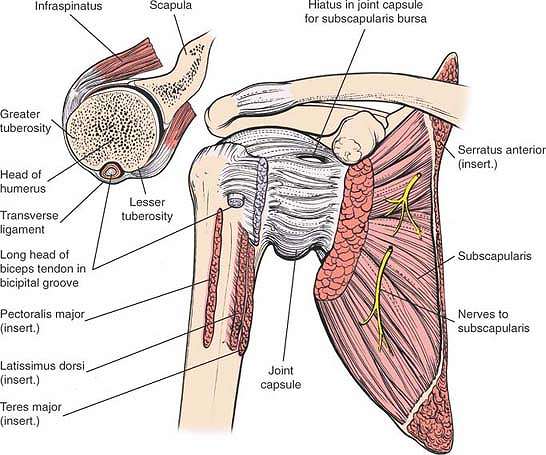
The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip.
Bicipital groove nerve. In order to accurately diagnosis and treat the patient shoulder arthroscopy was performed using standard posterior and anterior portals. From the posterior portal a fusiform mass parallel and adjacent to the long head of the biceps tendon was observed figure figure2a. D groeve a groove between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus for passage of the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral.
The bicipital groove intertubercular groove sulcus intertubercularis is a deep groove on the humerus that separates the greater tubercle from the lesser tubercle the bicipital groove lodges the long tendon of the biceps brachii between the tendon of the pectoralis major on the lateral lip and the tendon of the teres major on the medial lip. Defined three distinct anatomic zones of the bicipital groove. The surface marking of the nerve is along a line from the medial bicipital groove behind coracobrachialis to the point behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus where it is readily palpable. 1 taylor et al.
It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral. Zone 1extends from the articular margin to the distal margin of the subscapularis tendon zone 2 extends from the distal. The nerve courses through the lower part of the extensor compartment and disappears into the forearm by passing between the humeral and ulnar heads of. The bicipital groove which is bounded by the lesser tuberosity medially and the greater tuberosity laterally contains the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii muscle lhbt.
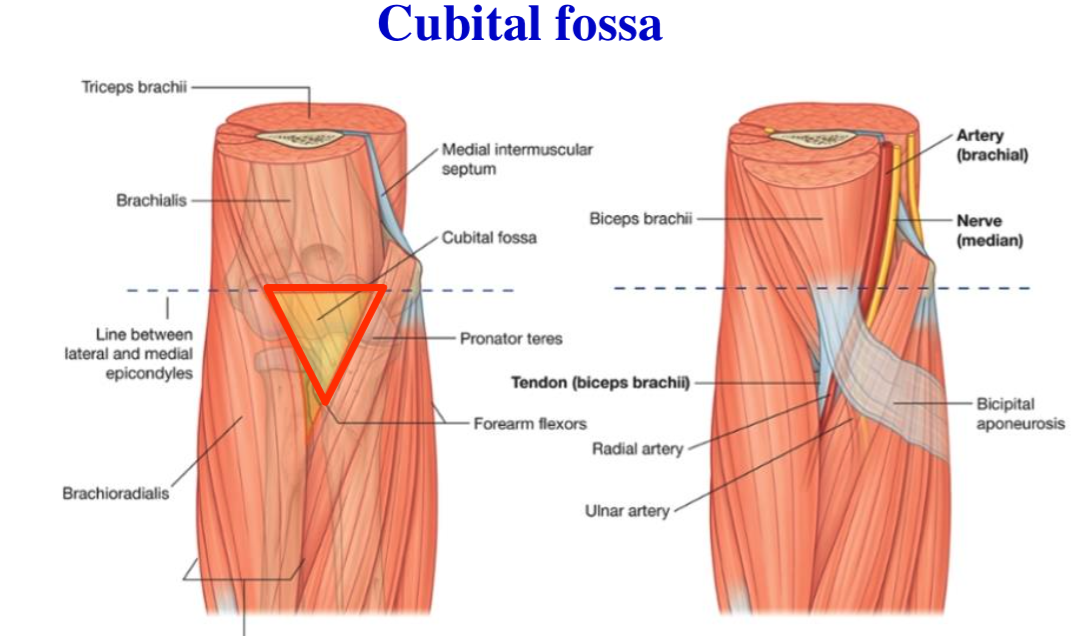
The radial sulcus also known as the musculospiral groove radial groove or spiral groove is a broad but shallow oblique depression for the radial nerve and deep brachial artery it is located on the center of the lateral border of the humerus bone. The median nerve traverses three successive arches or tunnels to enter the forearm deeply namely the bicipital aponeurosis pronator teres and flexor digitorum superficialis figures 41 6 and 41 7 it first passes under the bicipital aponeurosis which is a thick layer of fascia attaching the biceps brachii to the proximal forearm flexor mass. The biceps brachii muscle is supplied by the musculocutaneous nerve c5 c6 a branch of the brachial plexus. 2a by following the fusiform mass it was determined that it originated from the tendon at the bicipital groove figure.
The lateral bicipital groove contains the radial nerve. B manual muscle testing of the abductor pollicis longus for radial nerve entrapment in the lateral bicipital groove. Within the medial bicipital groove course the brachial artery and both the ulnar and median nerves.