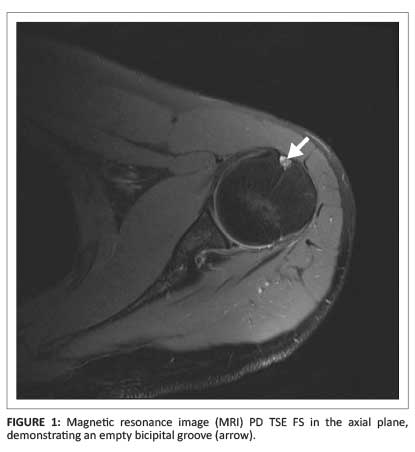
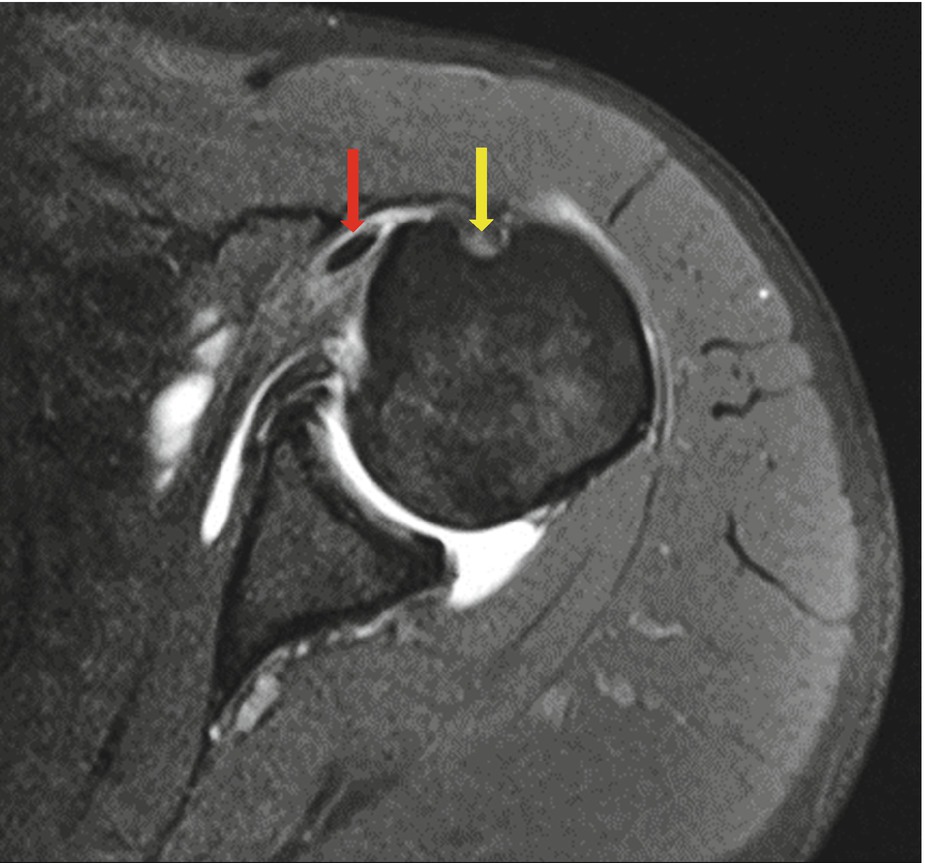
Bicipital Groove Mri

The bicipital groove is typically 4 6 mm deep 1.
Bicipital groove mri. Treatment initial management of patients with symptoms attributed to the lhbt begin with nonoperative therapies including modification of activity nonsteroidal anti inflammatory medication and physical therapy focused on any coexisting underlying. Duplication of the lhbt is a diagnostic dilemma in mri of patients with shoulder pain. 1 3b orthopaedics university of pennsylvania health system pennsylvania hospital philadelphia pa 19107 usa. A type i normal tendon b type ii hourglass shaped hypertrophic tendon with extension of fraying into bicipital groove c type iii partial tear or fraying involving less than 50 of tendon width at the intraarticular region without fraying in the bicipital groove d type iv partial tear involving more than 50 of.
High t2 signal intensity noted at the of this humeral head at the biceps groove. Biceps tendinitis is a disorder of the tendon around the long head of the biceps muscle. Mri allows preoperative assessment of the lhbt within and distal to the bicipital groove. Potential causes of pulley lesions include a congenital rotator interval defect 23 a supratubercular ridge as an osseous protrusion of the lesser tuberosity 24 or a shallow groove 5.
Abboud ja 1 bartolozzi ar widmer bj demola pm. Bicipital tenosynovitis is a pathological condition in which there is inflammation of the tendon sheaths that surround the biceps tendons. High t2 fluid signal intensity is noted around the thickened biceps tendon which is seen within its groove suggestive of tenosynovitis. Classification of the long head of the biceps tendon by arthroscopic findings.
The bicipital groove also known as the intertubercular sulcus or sulcus intertubercularis is the indentation between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus that lodges the biceps tendon. Bicipital tenosynovitis can be a result of many small tears resulting in inflammation over a period of a number of years or due to an acute injury to the biceps region. Thickened with intermediate high t2 signal intensity noted at the supraspinatus tendon suggestive of tendinosis. Biceps tendon laxity in the bicipital groove may lead to superior extension of degenerative changes in the rotator interval 7 18 20.
The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tubercle aswell as to the greater tubercle giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. 1 axial t1 weighted mr image shows shallow bicipital groove in presence of congenital absence of biceps tendon arrow. Inflammation of the biceps tendon within the intertubercular bicipital groove is called primary biceps.