Bicipital Groove Calcification
Biceps tendinitis is a disorder of the tendon around the long head of the biceps muscle.
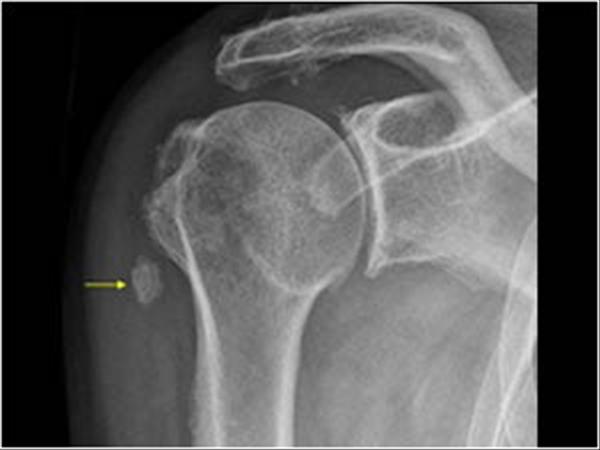
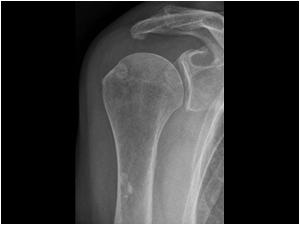
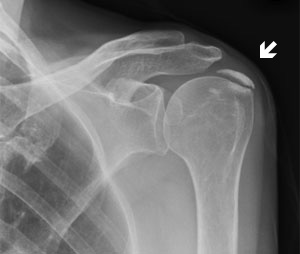
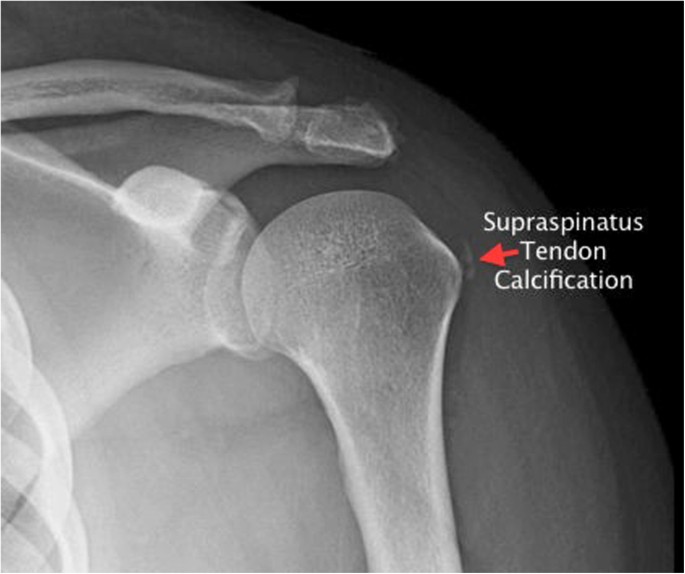
Bicipital groove calcification. The tendon is exposed on the anterior shoulder as it passes through the humeral bicipital groove and inserts onto the superior aspect of the labrum of the glenohu. Dfications ll biceps tendon groove radiographs also help to identify and localize small calcific deposits 12 mr imaging seems not to be a good method in this respect because of a relative lack mobile protons in calcifications 4 until now no large scale examination of the sono graphic findings of cuff calcifications had been undertaken. Calcific tendinitis is a common cause of shoulder complaints. 3 while mri showed tendinosis of the supraspinatus tendon without calcification.
Formation of bony bridge over the bicipital groove may also be caused by repetitive strain on the subscapularis supraspinatus muscles and pectoralis major muscle resulting in microtrauma during biomechanical movements of the shoulder and ultimately leading to calcification and ossification of these fibres. Inflammation of the biceps tendon within the intertubercular bicipital groove is called primary biceps. Bicipital tendinitis or biceps tendinitis is an inflammatory process of the long head of the biceps tendon and is a common cause of shoulder pain due to its position and function. Loose bodies in the bicipital groove pitfalls.
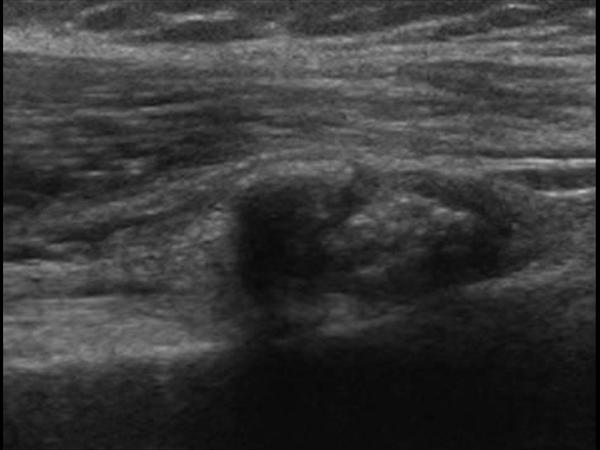
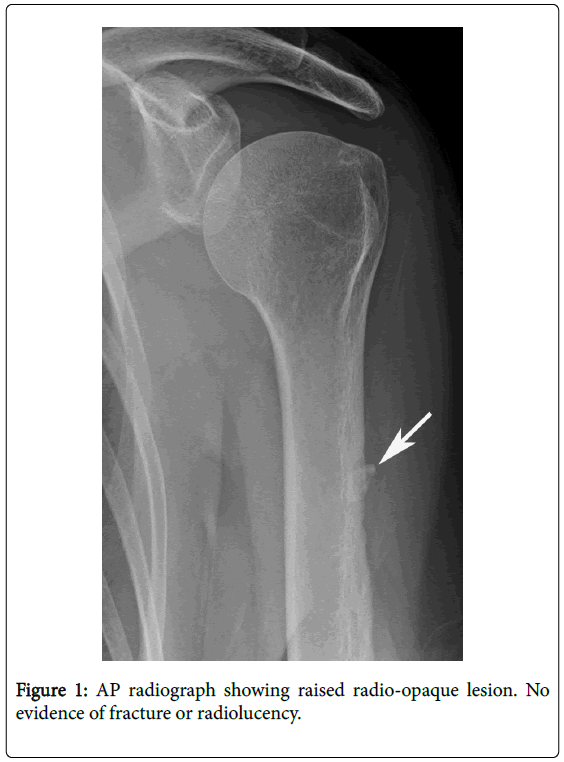
Ct confirmed the presence of a calcific deposit in the lbt site distal to the bicipital groove fig. Calcifications anterior of the biceps tendon longitudinal. 1 it is characterized by the presence of calcific deposits in the tendons mostly affecting the rotator cuff especially the supraspinatus tendon. The radiologic records of the plain radiographs us ct and mri were reviewed for the presence of structural abnormalities in the painful shoulder.
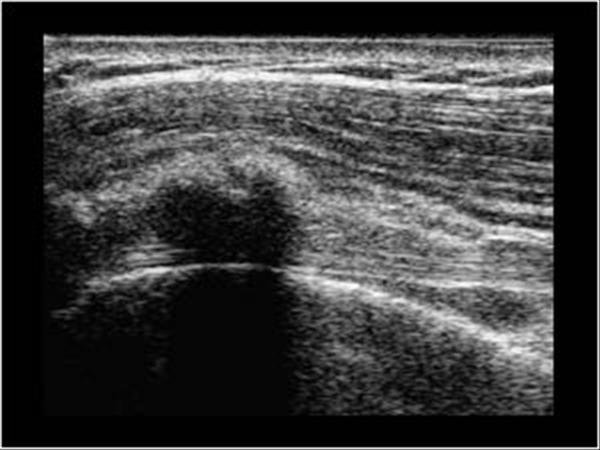
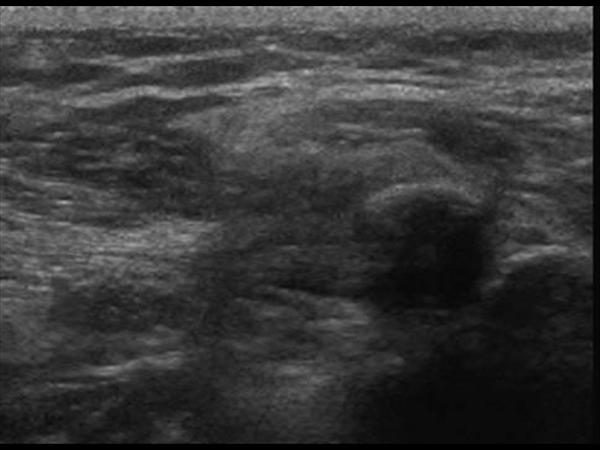
When examining the biceps region radiologically in cases of bicipital tenosynovitis there will be significant calcification of the tendon and presence of bone spurs in the intertubercular groove. Calcifications in the pectoralis major insertion that should not be mistaken for loose bodies in the biceps tendon sheath. And the acromion are particularly useful to the sonographer. Common rotator cuff pathology seen with sonography includes tears tendinitis impingement and calcification.
Ultrasound us and computed tomography revealed a long blade shaped circumscribed cloudy and irregular dense calcific deposit in the lbt site distal to the bicipital groove. Marked tenderness to palpation was present at the biceps tendon adjacent to the bicipital groove. The most common treatment for bicipital tenosynovitis is conservative treatment with physical therapy and exercises.